Do diesel engines have catalytic converters? Yes, diesel engines do have catalytic converters. It is a crucial component in minimizing exhaust emissions and meeting environmental regulations.
Catalytic converters in diesel engines help reduce harmful pollutants such as nitrogen oxides, carbon monoxide, and hydrocarbons, converting them into less harmful substances. The device contains precious metals like platinum, palladium, and rhodium, which facilitate chemical reactions to break down pollutants.
This technology is vital in reducing the environmental impact of diesel engines and ensuring compliance with emission standards. Diesel engines have evolved to incorporate catalytic converters as a standard feature in modern vehicles, highlighting their significant role in reducing harmful emissions. The integration of catalytic converters demonstrates the commitment of diesel engine manufacturers to environmental conservation and sustainability.
Diesel Engines Overview
Do diesel engines have catalytic converters? Diesel engines do not have catalytic converters like gasoline engines do. However, they have a different technology to minimize emissions. Diesel engines work by compressing air and fuel, rather than using a spark plug to ignite the fuel. This high compression causes the fuel to ignite and burn, creating the power to move the vehicle.
In terms of emissions, diesel engines produce nitrogen oxides and particulate matter. To reduce these emissions, diesel engines use selective catalytic reduction (SCR) and diesel particulate filters (DPF). SCR uses a urea-based solution to convert nitrogen oxides into harmless nitrogen and water, while DPF captures and burns particulate matter. Both technologies are crucial in reducing the environmental impact of diesel engines.

Credit: www.legendsmeltingrecycling.com
Catalytic Converters In Gasoline Vs. Diesel Engines
Catalytic Converters in Gasoline Engines work by converting harmful gases into less harmful gases, reducing emissions. These converters play a vital role in reducing air pollution. They mainly target carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, and unburned hydrocarbons. With a chemical reaction, these gases are converted into carbon dioxide, nitrogen, and water vapor.
On the other hand, diesel engines emit higher levels of nitrogen oxides and particulate matter. However, they do not have traditional catalytic converters like gasoline engines. Instead, they use diesel oxidation catalysts and diesel particulate filters. These components are designed to reduce emissions and comply with emission standards.
Differences in Emissions between diesel and gasoline engines are significant. While both engines use emission control systems, the pollutants they target and the methods they use are different. Understanding these differences is crucial for environmental and regulatory purposes.
Do Diesel Engines Have Catalytic Converters?
Diesel engines do have catalytic converters to reduce emissions. They work by converting harmful gases into less harmful ones. The catalytic converter in diesel engines helps to clean up the exhaust, improving air quality.
| Diesel Engines and Catalytic Converters |
| In the early days, diesel engines did not have catalytic converters. Catalytic converters were mainly found in gasoline vehicles. Modern diesel engines, however, have evolved to include catalytic converters to reduce emissions. |
Benefits Of Catalytic Converters In Diesel Engines
Catalytic converters in diesel engines offer numerous benefits, especially in terms of reducing harmful emissions and minimizing the environmental impact. These converters play a crucial role in converting toxic gases and pollutants produced during combustion into less harmful substances. By utilizing precious metals such as platinum, palladium, and rhodium, catalytic converters assist in breaking down harmful nitrogen oxides (NOx), carbon monoxide (CO), and unburned hydrocarbons (HC).
One of the key advantages is the reduction of harmful emissions, which helps in improving air quality and reduces the impact on the environment. Catalytic converters efficiently convert NOx compounds into nitrogen and oxygen, significantly reducing their adverse effects on health and the ozone layer. Additionally, they convert carbon monoxide into less dangerous carbon dioxide, minimizing the risk of respiratory issues and climate change.
Moreover, by reducing unburned hydrocarbons, catalytic converters assist in curbing the formation of smog and particulate matter, leading to cleaner and healthier surroundings. Overall, the inclusion of catalytic converters in diesel engines is crucial for achieving sustainable and eco-friendly transportation solutions.
Challenges And Limitations
Diesel engines face certain challenges and limitations when it comes to the use of catalytic converters. One of the main challenges is the impact of sulfur content. High levels of sulfur in diesel fuel can hinder the effectiveness of the catalytic converter, leading to reduced performance. Moreover, the sulfur can cause the converter to deteriorate over time, requiring frequent maintenance and replacement.
The sulfur content in diesel fuel affects the efficiency of the catalytic converter. Sulfur can poison the converter’s active sites, inhibiting the chemical reactions required for emission reduction. Additionally, it can deactivate the converter’s catalyst, making it less effective in converting harmful pollutants into less harmful substances. Controlling the sulfur content in diesel fuel is, therefore, crucial to ensuring optimal catalytic converter performance and reducing emissions.
In order to maintain the functionality of the catalytic converter, a regeneration process is necessary. This process involves periodically raising the exhaust gas temperature to burn off accumulated particles and restore the catalyst’s activity. However, the diesel engine’s relatively low exhaust gas temperature poses a challenge for efficient regeneration. To overcome this limitation, certain diesel engine designs employ additional components or technologies, such as diesel particulate filters and exhaust gas recirculation systems, to aid in the regeneration process.
Technological Advances
|
Diesel engines commonly have catalytic converters that aid in reducing harmful emissions. Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) technology helps in converting harmful nitrogen oxides into nitrogen and water. Diesel Particulate Filters (DPF) trap particulate matter, reducing pollution from diesel engines. |
Future Trends
Future Trends:
Diverse laws drive emission standards, pushing innovation in catalytic converters. Various advancements are being made to meet stricter regulations. Nano-coating technology and new catalyst materials are emerging. Reduced precious metal usage and improved thermal management techniques are being pursued.
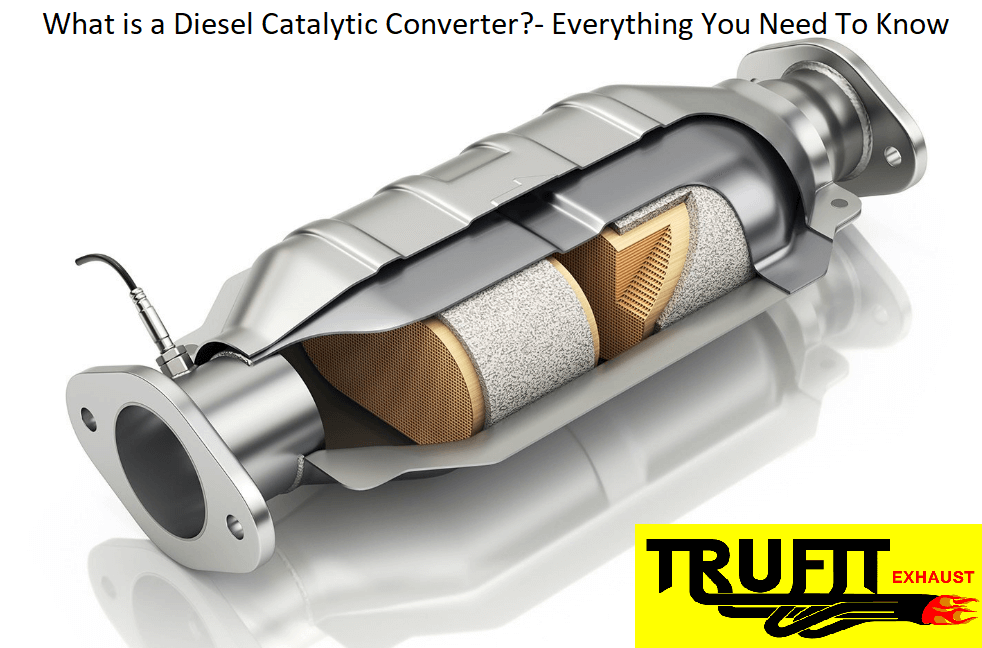
Credit: www.trufitexhaust.com.au

Credit: www.legendsmeltingrecycling.com
Frequently Asked Questions On Do Diesel Engines Have Catalytic Converters
Do Diesel Engines Have Catalytic Converters?
Yes, diesel engines do have catalytic converters. However, the design and function of the catalytic converter in a diesel engine differs from that of a gasoline engine. Diesel catalytic converters are specifically designed to reduce the emission of nitrogen oxide (NOx) and particulate matter (PM) from diesel exhaust.
Why Are Catalytic Converters Important In Diesel Engines?
Catalytic converters are crucial in diesel engines because they help to reduce harmful emissions. They convert pollutants like nitrogen oxides, carbon monoxide, and unburned hydrocarbons into less harmful substances. By using a catalyst, catalytic converters enable diesel engines to meet emission standards and contribute to cleaner air.
How Does A Catalytic Converter Work In A Diesel Engine?
In a diesel engine, a catalytic converter works by using a catalyst to facilitate chemical reactions that convert harmful pollutants into less harmful compounds. The exhaust gases pass through the catalyst, where chemical reactions occur, breaking down the pollutants. This process helps to reduce harmful emissions and improve air quality.
Can A Diesel Engine Run Without A Catalytic Converter?
Yes, a diesel engine can technically run without a catalytic converter. However, doing so would result in significantly higher emissions of harmful pollutants, such as nitrogen oxides and particulate matter. Additionally, running a diesel engine without a catalytic converter may also lead to non-compliance with emission standards and potentially result in legal consequences.
Conclusion
Diesel engines do have catalytic converters, essential for reducing harmful emissions. Understanding their role is vital for eco-friendly driving practices. By maintaining and ensuring the proper function of catalytic converters, you contribute to a cleaner environment and better air quality.
Make informed choices for a sustainable future.